Adapting Positional Play to Different Formations: A Guide for Coaches
Adapting positional play to different formations is a key aspect of modern football. Positional play is a tactical concept that involves creating numerical superiority on the pitch by occupying strategic areas. It requires players to occupy specific positions and receive the ball with passing options, and it has been implemented effectively by top coaches like Pep Guardiola.
Understanding positional play is crucial for coaches who want to adapt it to different formations. Key elements of positional play include creating space, maintaining possession, and exploiting the opposition’s weaknesses. Coaches need to understand how different formations affect the way positional play is implemented and how it can be adapted to suit different players and situations.
Key Takeaways:
- Adapting positional play to different formations is crucial in modern football.
- Understanding the key elements of positional play, such as creating space and maintaining possession, is essential for coaches.
- Coaches need to be able to adapt positional play to different formations and situations to make the most of their players’ strengths.
Understanding Positional Play
Positional play is a tactical concept in football that involves players occupying specific positions on the pitch to gain numerical superiority and create scoring opportunities. The idea behind positional play is to create passing options for the player in possession of the ball, allowing them to maintain possession and create scoring opportunities.
The concept of positional play was first introduced by Rinus Michels, a Dutch football coach, who implemented it in his team, Ajax Amsterdam, in the 1970s. Later, Johan Cruyff, a former player of Michels, further developed the concept and used it to great effect during his time as a coach of Barcelona.
Pep Guardiola, another disciple of Cruyff, has also implemented positional play in his teams, including Barcelona and Manchester City. Guardiola’s teams are known for their possession-based style of play, where players move the ball quickly and efficiently, creating space and opportunities to score.
The key to positional play is to develop relationships and rotations between players, allowing them to move and create space for each other. Players must maintain their positions, but also be able to move into space when necessary, creating passing options for their teammates.
In a positional game, players must be aware of their surroundings and the movement of their teammates and opponents. They must be able to anticipate the movements of their opponents and react quickly to create scoring opportunities.
To implement positional play successfully, coaches must focus on developing the tactical concepts and principles necessary for their team to play this style of football. They must also focus on developing the technical skills of their players, including passing, dribbling, and ball control.
Overall, positional play is a tactical concept that requires a high level of skill and understanding from players and coaches alike. When implemented correctly, it can create a dynamic and exciting style of football that is both effective and enjoyable to watch.
Key Elements of Positional Play
Positional play is a game of player positioning for a strategic purpose. It is not possession for the sake of possession. The main aim of positional play is to create numerical and positional superiority to dominate the game. The following are key elements of positional play:
Structure and Positioning
Structure and positioning are crucial elements of positional play. The team must have a clear plan and structure that all players can follow. The players must be positioned strategically to create space and opportunities to receive the ball. The team must also be able to cover the field both in depth and width to create numerical superiority.
Overload and Numerical Superiority
Positional play is all about creating numerical superiority. The team must be able to create overloads in different areas of the field to create opportunities to exploit the opponent’s defense. The team must also be able to create numerical superiority in different phases of the game such as attacking, defending, and transition.
Qualitative Superiority
Positional play is not just about creating numerical superiority, but also qualitative superiority. The team must be able to create opportunities to exploit the opponent’s weaknesses and create advantages for themselves. The team must also be able to create opportunities to counter-press and regain possession of the ball.
Fluidity and Collectivity
Positional play requires fluidity and collectivity. The team must be able to move the ball quickly and efficiently to create opportunities to exploit the opponent’s defense. The team must also be able to work together as a unit to create opportunities for each other and to defend as a team.
Defensive Shape and Counter-Pressing
Positional play is not just about attacking, but also about defending. The team must be able to maintain a solid defensive shape and be able to counter-press to regain possession of the ball quickly. The team must also be able to create a free man to create opportunities to transition from defense to attack quickly.
In summary, positional play is a game of player positioning for a strategic purpose. It requires structure, positioning, overload, numerical and qualitative superiority, fluidity, collectivity, defensive shape, and counter-pressing. The team must be able to create opportunities to exploit the opponent’s weaknesses and create advantages for themselves while maintaining a solid defensive shape.
Adapting Positional Play to Different Formations
Positional play is a tactical concept that seeks to gain numerical superiority by occupying strategic areas on the pitch. It requires players to occupy specific positions and receive the ball with passing options. Adapting positional play to different formations is essential for a team to be successful.
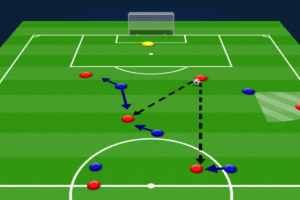
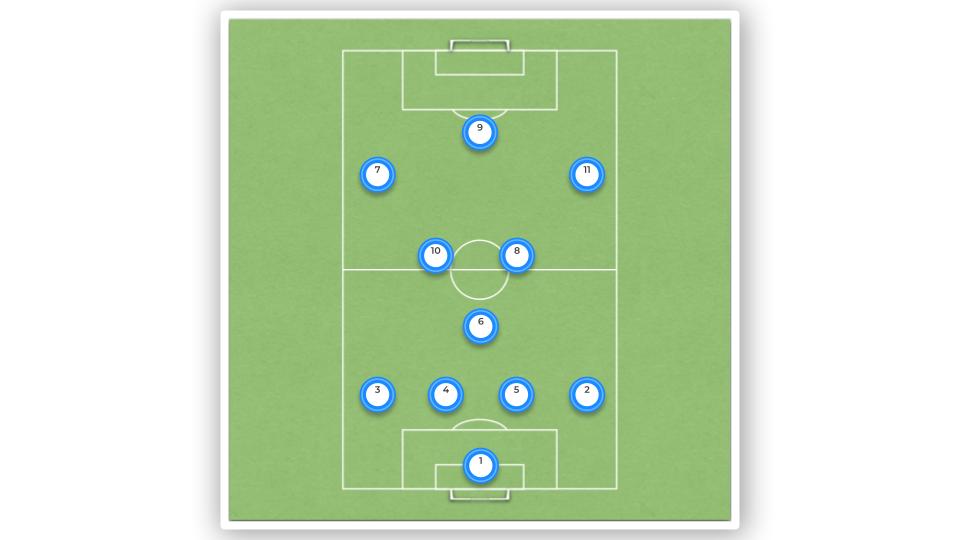
One common formation that is used in positional play is the 4-3-3. In this formation, the team structure is fluid, and the central midfielders are crucial to the success of the strategy. The wide players are also important as they occupy the touchline and create passing triangles with their teammates. The passing combinations and positional rotation are well-orchestrated, and the team looks to pass the ball quickly and efficiently to counter-attack.
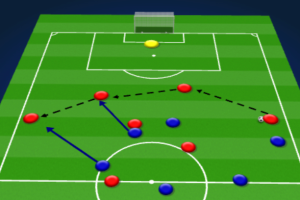
Another popular formation that can be used in positional play is the 4-2-3-1. In this formation, the attacking midfielders are essential to the team’s success. They occupy the wide positions and provide movement off the ball to create passing options for their teammates. The full-backs are also important as they provide width to the team and occupy the wide positions.
When adapting positional play to different formations, it is essential to consider the player abilities and the tactical nuances of each formation. For example, a team with young players may struggle to execute positional play in a direct style, and it may be better to focus on counter-attacking.
It is also important to consider the point of attack when adapting positional play to different formations. For example, in a 4-3-3 formation, the team looks to occupy the wide positions to create passing options, while in a 4-2-3-1 formation, the team looks to occupy the central areas of the pitch to create scoring opportunities.
In conclusion, adapting positional play to different formations requires a thorough understanding of the tactical nuances and player abilities of each formation. By implementing well-orchestrated passing combinations and positional rotation, a team can successfully execute positional play in any formation and gain a numerical advantage on the pitch.
Role of Coaches and Players
Adapting positional play to different formations requires a collaborative effort between coaches and players. Coaches must have a deep understanding of the sport and the technical skills required to play different positions. They must also have the ability to communicate effectively with their teammates and manager to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Players, on the other hand, must be able to adapt to different formations and play styles. They must possess the technical skills required to play different positions and be able to build relationships with their teammates. This includes wingers, who must be able to work closely with their full-backs to create opportunities on the flanks.
The role of the coach is to create a game plan that takes into account the strengths and weaknesses of the team. They must also be able to make adjustments on the fly based on the opponent’s formation and tactics. This requires a deep understanding of the game and the ability to read the flow of the match.
Players, on the other hand, must be able to execute the coach’s game plan and adapt to changing circumstances on the field. This requires a high level of technical ability and the ability to read the game. They must also be able to work together as a team and build strong relationships with their teammates.
In summary, adapting positional play to different formations requires a strong collaboration between coaches and players. Coaches must have a deep understanding of the sport and be able to communicate effectively with their teammates and manager. Players must possess the technical skills required to play different positions and be able to build relationships with their teammates. Together, they can create a game plan that takes into account the strengths and weaknesses of the team and adapt to changing circumstances on the field.
Positional Play in Professional Football
Positional play is a tactical concept that has gained popularity in modern football. The idea behind positional play is to create numerical superiority by occupying strategic areas on the pitch. Pep Guardiola, the former Barcelona and current Manchester City manager, is widely regarded as the pioneer of this tactical approach.
Guardiola’s positional play requires players to occupy specific positions and receive the ball with passing options. The aim is to create passing triangles or diamonds, which allow the team to progress possession through the thirds. The system also involves the use of positional rotation and interchange, where players change positions to create space and confusion in the opposition’s defensive structure.
Ajax, Real Madrid, and Manchester City are among the teams that have successfully implemented positional play in recent years. The system requires intelligent and technically proficient players who can read the game and make quick decisions. It also requires a high level of fitness, as players are required to constantly move and interchange positions.
One of the key benefits of positional play is that it allows teams to control the game and dominate possession. It also enables teams to create scoring opportunities by breaking down the opposition’s defensive structure. However, the system does have its weaknesses, particularly against teams that employ a high press or counter-attacking strategy.
The success of positional play largely depends on the formation used by the team. For instance, Guardiola has adapted his system to suit the 4-3-3 formation used by Barcelona and the 4-1-4-1 formation used by Manchester City. Sergiño Dest, the right-back for Barcelona, is an example of a player who has thrived under positional play due to his ability to make overlapping runs and interchange positions with the right-winger.
In summary, positional play is a tactical approach that seeks to gain numerical superiority by occupying strategic areas on the pitch. It requires intelligent and technically proficient players who can read the game and make quick decisions. The success of the system largely depends on the formation used by the team and the ability of the players to adapt to the system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the principles of positional play?
Positional play is a tactical concept that seeks to gain numerical superiority by occupying strategic areas on the pitch. The fundamental principle of positional play is the search for superiority. There are various ways to gain superiority and various types of superiority that can be achieved. Once superiority is found, the team can use the situation to dominate the game. The superiorities we look to create in positional play can be an overload, isolation of a 1v1 mis-match, superior player positioning, the emergence of gaps/space in the defending team, or even a speed advantage.
How can you adjust positional play to different formations?
Adapting positional play to different formations requires a thorough understanding of the principles of the formation and the principles of positional play. The key is to maintain the fundamental principles of positional play while adjusting the positioning and movement of players to fit the formation. For example, in a 4-3-3 formation, the midfielders may need to adjust their positioning to provide passing options for the forwards. In a 3-5-2 formation, the wingbacks may need to push higher up the pitch to provide width in the attack.
What are some common mistakes when implementing positional play?
One common mistake is not having a clear plan or structure for the team to follow. Another mistake is players not understanding their roles and responsibilities within the system. In addition, positional play requires a high level of technical ability and fitness, so players who are not technically proficient or fit enough may struggle to implement the system effectively.
What are some effective drills for teaching positional play?
Effective drills for teaching positional play include small-sided games that emphasize positioning and movement, such as 4v4 or 5v5 games with specific restrictions on player movement. Other drills include passing and movement exercises that focus on maintaining possession and creating numerical superiority in specific areas of the field.
How does Pep Guardiola incorporate positional play into his coaching style?
Pep Guardiola is known for his use of positional play in his coaching style. He emphasizes the importance of maintaining possession and creating numerical superiority in specific areas of the field. Guardiola’s teams are known for their fluid movement and interchanging positions, which creates confusion for the opposition and allows his team to dominate possession and create scoring opportunities.
What is the difference between functional play and positional play in soccer?
Functional play focuses on specific roles and responsibilities within the team, such as a striker‘s role in the attack or a defender’s role in the defense. Positional play, on the other hand, emphasizes the importance of maintaining a specific shape and creating numerical superiority in specific areas of the field. While functional play is important, positional play allows for greater flexibility and creativity in the team’s overall approach to the game.