Soccer Game Model: A Comprehensive Guide for Club Coaches
I am always fascinated by the different strategies and tactics that coaches use to achieve success on the field. One of the most important concepts in modern soccer is the game model, which refers to the overarching approach that a team takes to the game. The game model encompasses everything from formation and positioning to pressing and counter-attacking, and it is designed to give players a clear sense of their roles and responsibilities on the field.
Developing a strong game model is critical for any team that wants to compete at the highest levels of the sport. By establishing a cohesive and effective style of play, coaches can help their players to perform at their best and maximize their chances of winning. However, creating a game model is not a simple process, and it requires a deep understanding of the game, as well as a willingness to experiment and adapt to changing circumstances.
So what exactly is a game model, and how can coaches develop one that works for their team? In this article, I will explore the key elements of a successful game model, as well as some of the strategies and techniques that coaches can use to create one. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of what it takes to develop a game model that can help your team to achieve its goals on the soccer field.
The Importance of a Soccer Game Model for a Coach?
A soccer game model is a framework developed by coaches to enhance the team’s performance in specific sub-phases of play. It is a tactical/strategic approach adopted by coaches to improve player functionality and performance on the field. In this section, I will discuss why coaches use game models and the benefits of using a game model in soccer.
Why Coaches Use Game Models
Coaches use game models to simplify the complex nature of soccer and provide a starting point for their team to play. A game model helps coaches to define a style of play and create predictability through preparation, planning, and training. It is a handy tool that coaches use to communicate their philosophy and tactics to the team.
Another reason why coaches use game models is to enhance the team’s strengths and minimize its weaknesses. By analyzing the team’s strengths and weaknesses, coaches can develop a game model that is suitable for the team’s characteristics. This helps the team to play to its strengths and overcome its weaknesses.
Benefits of Using a Game Model
Using a game model has several benefits for coaches, players, and teams. One of the main benefits is that it provides a framework for the team to play soccer. This framework helps the team to understand their roles and responsibilities on the field and simplifies the game for them.
Another benefit of using a game model is that it helps the team to be more flexible. A game model provides guidelines for the team to follow, but it also allows for variation and flexibility depending on the context of the game. This flexibility allows the team to adapt to different situations and be more competitive.
Using a game model also helps to improve communication among the team members. By having a clear understanding of the game model, players can communicate more effectively with each other on the field. This improves the team’s performance and helps them to accomplish their goals.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Game models provide a starting point for the team to play |
| Game models enhance the team’s strengths and minimize its weaknesses |
| Game models simplify the game for the team |
| Game models allow for flexibility and adaptation to different situations |
| Game models improve communication among team members |
Overall, using a game model is essential for any soccer team that wants to improve its performance on the field. It provides a framework for the team to play, enhances the team’s strengths, and minimizes its weaknesses. It simplifies the game for the team and allows for flexibility and adaptation to different situations. Using a game model improves communication among team members and helps the team to accomplish their goals.
Differences Between Systems of Play and a Game Model? Is a 4-3-3, or a 4-2-3-1 a Philosophy?
As a soccer coach, I have come across many terms that are used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Two such terms are ‘systems of play’ and ‘game model.’ While they might seem similar, there are significant differences between them.
A system of play refers to the formation or arrangement of players on the field. It is a tactical plan that a coach uses to organize his team, and it can vary depending on the opposition, the players’ strengths, and the coach’s philosophy. Some examples of systems of play include 4-4-2, 3-5-2, and 4-3-3.
On the other hand, a game model is a more comprehensive approach to coaching. It is a holistic view of how a team should play soccer, and it includes various aspects such as style of play, principles of play, and team culture. A game model is not a rigid formation but rather a flexible framework that allows for adaptation and creativity.
One way to understand the difference between systems of play and a game model is to think of systems of play as the ‘what’ and the game model as the ‘how.’ A system of play tells you what formation to use, but a game model tells you how to play within that formation.
Table: Differences Between Systems of Play and a Game Model
| Systems of Play | Game Model |
|---|---|
| Refers to the formation or arrangement of players on the field | A holistic view of how a team should play soccer |
| Is a tactical plan that a coach uses to organize his team | Includes various aspects such as style of play, principles of play, and team culture |
| Can vary depending on the opposition, the players’ strengths, and the coach’s philosophy | Is a flexible framework that allows for adaptation and creativity |
Overall, while systems of play and a game model are related, they are not the same thing. A system of play is a tactical plan that a coach uses to organize his team, while a game model is a holistic view of how a team should play soccer. Understanding the differences between these two concepts is crucial for any coach who wants to develop a successful team.
The Components of a Soccer Game Model – Organize Your Attack, Defense, and Transition Principle
Defining a Soccer Game Model
A soccer game model is a tactical framework that defines how a team plays the game of soccer. As a coach, I believe that a game model is essential for a team’s success. It provides a guideline for the team’s style of play, principles of play, and tactical approach. The game model should reflect the coach’s philosophy and the team’s strengths.
The Four Moments of the Game
The game of soccer can be divided into four moments: 1. Possession phase: When a team has the ball 2. Transition phase: When the ball changes possession. You can break this down into two parts (when you’ve just won the ball, and when you’ve just lost the ball) 3. Non-possession phase: When the opposition has the ball 4. Set-piece phase: When the ball is out of play, and a set-piece is awarded
As a coach, I believe that understanding the four moments of the game is crucial in building a game model. Each moment requires a different tactical approach.
Tactical Aspects of a Game Model
A game model should address the tactical aspects of the game. This includes the team’s formation, principles of play, and systems of play. The formation refers to the team’s shape on the field. The principles of play refer to the team’s style of play, such as possession-based or counter-attacking. The systems of play refer to the team’s tactical approach, such as a high press or a low block. As a coach, I believe that a game model should be flexible and adaptable. It should be able to vary based on the context of the game and the opposition’s strengths and weaknesses.
| Key Points |
|---|
| A soccer game model is a tactical framework that defines how a team plays the game of soccer. |
| The game of soccer can be divided into four moments: possession, transition, non-possession, and set-piece. |
| The game of soccer can be divided into three phases: attacking, defensive, and transition. |
| A game model should address the team’s formation, principles of play, and systems of play. |
| A game model should be flexible and adaptable. |
How to Build a Game Model to Play Soccer “Your Way”
Building a soccer game model is a crucial step for any coach looking to improve their team’s performance. In this section, While I’ll show you, my game model, later in this article, now I’ll give a general guide.
I will outline the key steps in building a soccer game model, including starting points, methodology and frameworks, flexible play systems, communication, and training.
Starting Points
The starting point for building a soccer game model is to define the philosophy and style of play that the team will adopt. This should be based on the coach’s vision of how they want the team to play soccer. It is important to attend webinars and download resources that will enhance your knowledge of soccer training and build a soccer game model.
Methodology and Frameworks
The methodology and frameworks used in building a soccer game model should be based on the team’s strengths and weaknesses. This will help to simplify the process of building a soccer game model and make it more effective. UEFA has sub-principles that can help coaches create a soccer game model that is suitable for their team.
Flexible Systems of Play
Flexible systems of play are important in building a soccer game model as they allow for variations in tactics and formations depending on the opponent and the phase of the game. Coaches should consider different formations, such as the 4-3-3 or 4-2-3-1, and how they can be adapted to suit the team’s style of play.
Communication and Training
Effective communication and training are essential in building a successful soccer game model. Coaches should communicate their vision and philosophy to the team and ensure that all players understand their roles and responsibilities. Training sessions should be designed to enhance the team’s technical, tactical, and psychological strengths and address any weaknesses.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Define the philosophy and style of play that the team will adopt |
| Use methodology and frameworks that simplify the process of building a soccer game model |
| Consider flexible systems of play that can be adapted to suit the team’s style of play |
| Ensure effective communication and training to enhance the team’s strengths and address any weaknesses |
Building a soccer game model is an ongoing process that requires constant evaluation and adjustment. Coaches should attend webinars, download resources, and study the game to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and techniques. By following these guidelines, coaches can build a soccer game model that will help their team to play soccer at a competitive level.
Tactical Periodization and its Impact on a Game Model
Game Model
As a soccer coach, I understand that the game model is the foundation of tactical periodization. It defines how the team should play, and how the team should react to different situations in the game. The game model is usually divided into different phases, such as attacking, defending, and transitioning. Each phase is further divided into sub-phases, which provide more detail on how the team should behave in specific situations.
Training Model
The training model is the second crucial component of tactical periodization. It is the way the coach teaches the game model to the team. The training model is designed to improve the players’ skills, fitness, and decision-making abilities while ensuring that they understand the game model. The training model should be based on the game model, and all training sessions should be designed to improve the players’ understanding and execution of the game model.
Impact on Game Model
Tactical periodization has a significant impact on the game model. It ensures that the team’s training sessions are aligned with the game model, and that the players understand how to execute the game model in different situations. Tactical periodization also ensures that the team is physically and mentally prepared to play the game model effectively.
One of the most significant benefits of tactical periodization is that it allows the coach to improve all other attributes, such as technical skills, conditioning, and decision-making, at the same time as improving the players’ understanding of the game model.
This means that the team can develop a more complete and well-rounded playing style, which is more difficult for opponents to counter. In summary, tactical periodization is a proven successful training model that has a significant impact on the game model. It ensures that the team’s training sessions are aligned with the game model, and that the players understand how to execute the game model in different situations. Tactical periodization also allows the coach to improve all other attributes at the same time as improving the players’ understanding of the game model.
Examples of a Football Game Model – Elite Tactic Models that Might Inspire Your Technical Game Model
As a soccer coach, I have found that developing a game model is crucial to the success of a team. Here are a few examples of game models that have been successful in the world of soccer:
Barcelona’s Tiki-Taka
Barcelona’s Tiki-Taka game model is based on short, quick passes and maintaining possession of the ball. This style of play requires players to move and create space for their teammates constantly. The Tiki-Taka game model has been highly successful for Barcelona, as they have won numerous titles and dominated the world of soccer for many years.
Germany’s Counter-Pressing
Germany’s game model is based on counter-pressing, which involves quickly regaining possession of the ball after losing it. This style of play requires players to press high up the field and win the ball back quickly. Germany’s counter-pressing game model was highly successful in the 2014 World Cup, as they won the tournament with ease.
Atletico Madrid’s Defensive Game Model
Atletico Madrid’s game model is based on a strong defensive structure and counter-attacking football. This style of play requires players to be highly disciplined and organized defensively, while also being able to transition to attack when the ball is won quickly. Atletico Madrid’s defensive game model has been highly successful in recent years, as they have consistently challenged for titles in the highly competitive Spanish league. Overall, game models can vary greatly depending on a team’s strengths and weaknesses. By analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of a team, a coach can develop a game model that is tailored to their specific needs. Table 1 below summarizes the key points of each game model discussed in this section.
| Game Model | Description | Success |
|---|---|---|
| Tiki-Taka | Short, quick passes and maintaining possession of the ball | Highly successful for Barcelona |
| Counter-Pressing | Quickly regaining possession of the ball after losing it | Highly successful for Germany in the 2014 World Cup |
| Defensive Game Model | Strong defensive structure and counter-attacking football | Highly successful for Atletico Madrid in recent years |
My Game Model and the Process I Took to Create It
Earlier I gave some basic info on writing a game model. Here’s a specific game model of mine, and how I went about creating it.
Define Your ‘Philosophy’
Now, “philosophy” isn’t really a word I’d use outside of this article. However, it doesn’t really matter what you call it.
The first step of writing your game model is to write down how your ideal team would play.
If you’re writing a general game model that you’ll take with you from club to club, you can go crazy with your ideal.
However, if you’re already in a club, or writing for a club, you’ll be a little limited (not that there’s anything wrong with that).
When I take on a new job at a club, I always look to create a new game model. This isn’t always built from scratch, as my general philosophy on how I want my teams to look (and how I think you win games) largely stays the same year after year while slowly developing.
I tweak how I want to play with a few pre-existing factors. Mainly:
- The club I’m at: Some clubs have a pre-existing philosophy on how they want to play. In this case, it’s up to you to match what you’re doing with what they want. Now, it’s likely that if a club like that has hired you, you’re probably already a match. Same goes for training schedules. If you’re training once a week, you won’t be able to do too many crazy in-depth tactical tweaks.
- The players I have: For example, if I’ve got a lot of small technical players, I’m probably not going to look to hit the channels with long balls.
- The league I’m in: If you’re in a heavy pressing league, that might impact on how you play. Also, where and when the league takes place. A great example is the Australian A-Leagues. Matches are played in the middle of summer. Having a press-at-all-costs game model is a disaster waiting to happen.
Here’s a few ideas on how I want my teams to play football in an ideal world. It’s not a full list, but it’s a quick snippet.
| How I want to play with the ball | How I want to play without the ball |
| I want to find players between the lines, facing forwards, with options ahead of them | Win the ball back in the middle of the pitch |
| Comfortable on the ball | Press high and set traps |
| Lots of movement off the ball | Fight to win first and second balls |
| Generate one-on-one opportunities |
Do the same for your ideal team. How do you want them to play? Keep the list strict to the key elements. This will be used later on.
Break Down and Expand Your List to the Four Phases of Play
I like to start with the basic in/out possession stats – but, you can then break it down even more afterwards. Ideally, you’d break your list into the four phases of play (or three, if you include transition as only one phase).
I’d also suggest adding another section for restarts (set pieces, kickoffs, etc).

This is a lot easier said than done, so we’ll go a little deeper into what that looks like.
Break Down Phases of Play
To me, the easiest place to start is what you want to do with the ball. However, some would find it easier to do without.
Regardless, no matter where you start, the process is similar. Start with one of your phases, and go into greater detail.
I like to go into the following:
- Overall objective: What you want to do in that phase
- Break what you do in each third (in the image, I’ve called these phases, but I want to avoid doing that here so there’s no confusion): Where you’ll do it
- Principles in each third: How you’ll do it
- What success looks like in each third: How do you know if you’re successful or not
For example, here’s what I’ve done for my attacking phase.

As you can see, I’ve not gone over the top with instructions in each third – and in reality, some of those aren’t used as much as others.
But they’re all used to some degree.
I do the same process for each phase of play. Here is what that looks like for a club I’ve been at.



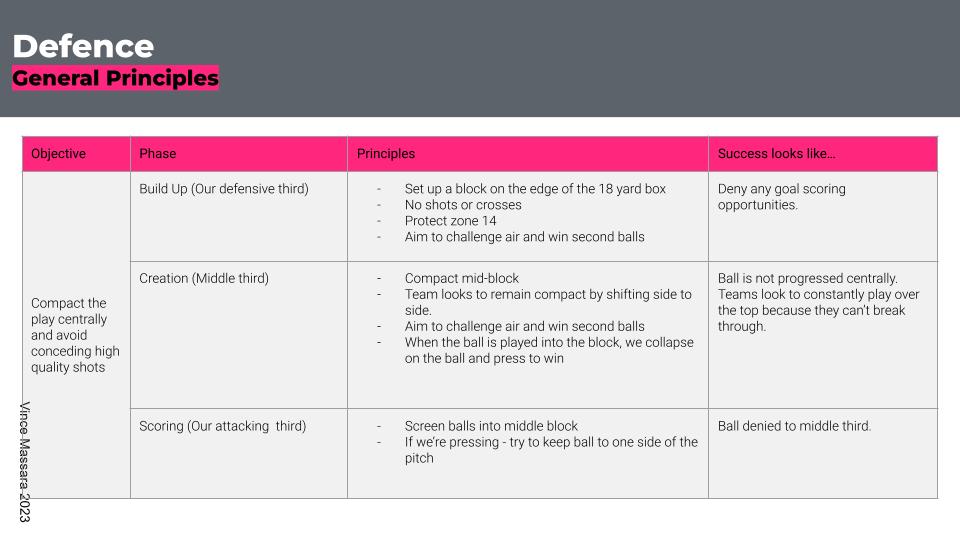
Break Down Each Principle
Now, what you’ve got is enough for the basics. However, if you want to go a little deeper, break down each of the key principles and include examples, and coaching points.

I use this as a guide to show assistant coaches, and the players. Someimes there’s going to be a few words and phrases unique to you – so it’s best to make sure everyone involved with your team knows what you’re talking about.
Once you’ve got all that down, you’re basically done.
Training Schedule
There’s plenty of ways you can plan your training around your game model – this depends on how your club trains, how many days you train, and how much help you’ve got.
For example, my club only trains twice a week. So we train one day on the middle third and the other day on the final/first third. This works for us, but I’ve trained with different schedules before.
Final Thoughts
As I conclude this article on the Soccer Game Model, I want to emphasize thee importance of having a clear and well-defined game plan. The Game Model is not just a theoretical framework, but a practical tool that can help teams succeed. By developing a consistent style of play and a shared understanding of roles and responsibilities, players can work together more effectively and make better decisions.
One of the key benefits of the Game Model is that it allows coaches to tailor their approach to the strengths and weaknesses of their team. By analyzing the team’s performance data and identifying areas for improvement, coaches can make targeted adjustments to their tactics and training methods. This can help the team to progress and develop over time, and ultimately achieve their goals.
| Benefits of the Game Model | Challenges of the Game Model |
|---|---|
| Provides a clear and consistent style of play | Requires buy-in and commitment from all players |
| Helps players to understand their roles and responsibilities | May not be suitable for all teams and playing styles |
| Allows for targeted adjustments based on performance data | Requires ongoing analysis and evaluation |
Ultimately, the success of the Game Model depends on the coach’s ability to communicate their vision and motivate their players to execute it. By fostering a culture of teamwork, discipline, and creativity, coaches can create a winning environment that inspires players to reach their full potential. As a coach, I believe that the Game Model is an essential tool for any team that wants to compete at a high level, and I look forward to continuing to refine and improve my own approach to coaching.